
Knowledge Treasures
The Strategic Intelligence of Plants
The hidden potential of plants
AT A TIME WHEN CLIMATE CHANGE AND ENVIRONMENTAL AWARENESS ARE AMONG THE MOST IMPORTANT GLOBAL CHALLENGES, PLANTS OFFER SOLUTIONS THAT GO FAR BEYOND OUR CONVENTIONAL THINKING.
From the age of bacteria and viruses to the diversity of life today, plants have played a central role in the history of our planet. Not only are they the base of our food chain, they are also the masters of carbon sequestration through photosynthesis. This ability of plants to store CO2 and convert it into vital resources is one of the greatest hopes in the fight against climate change.

A natural laboratory
The leaves of a plant are more than just greenery. They are natural, sophisticated chemical laboratories that use sunlight and carbon from the atmosphere to produce a variety of substances essential to nature and human life. This process is called photosynthesis, and it is essential to our survival.
How does photosynthesis work?
Plants absorb the CO2 that we humans exhale along with water through their leaves and convert it into sugars and oxygen in a chemical process with the help of sunlight. The oxygen is a kind of “waste product” that the plant itself does not need and therefore releases back into the environment. This allows us humans to use it for breathing.
The sugar produced, on the other hand, is needed by the plants as a nutrient. It also serves as food for the rich soil life that promotes plant health and growth. The soil is inhabited by what are called microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi and algae. These microorganisms are responsible for the presence in the soil of many substances vital to plants, such as phosphorus and ammonia. Without these microorganisms in the soil, plants could not survive.
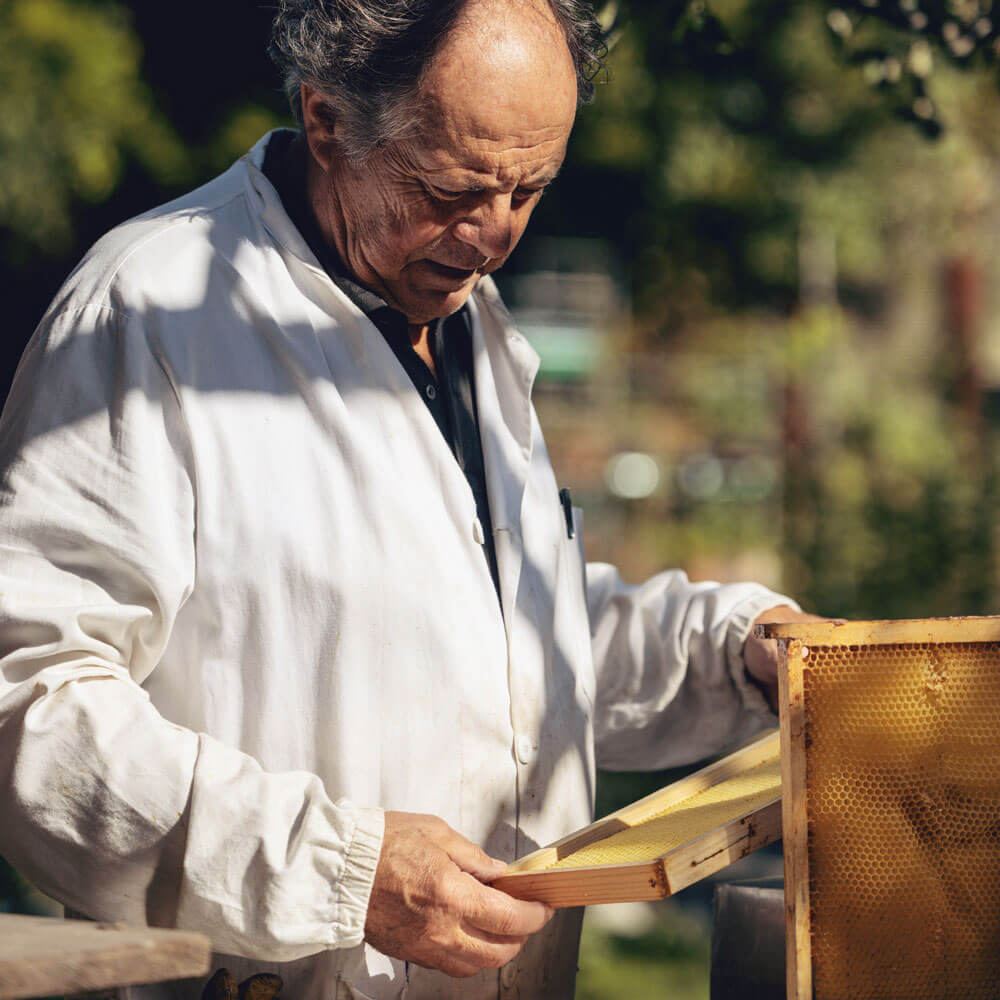

Nature is the world’s most intelligent high-tech laboratory.
Erb. Dipl. Dr. Joseph Franz · Founder
What is the role of biodiversity?
In addition to microorganisms, insects are crucial to the reproduction and survival of the plant world, as they pollinate plants. However, due to monocultures and other human interventions in nature, insect diversity has declined by up to 75% in some areas. As a result, plants are also suffering. In order to combat climate change, it is therefore important to preserve not only the biodiversity of plants, but also that of insects.

The Intelligence of Plants
Plants have more than 20 sensory organs that allow them to perceive and respond to their environment. Plants use these sensory organs to communicate not only within their cells, but also with other living organisms and their environment.
The ability of plants to exchange signals via electrical impulses and chemical signals shows that they have a highly complex network of interactions. This proves that plants are independent and intelligent organisms that have different, clear strategies for dealing with their environment:
Survival artists
Plants use electrical and hydraulic systems to exchange vital information between roots and leaves. This allows them to adapt quickly to changes such as a lack of water. If the roots cannot absorb enough water, they send a signal to close the flowers and leaves. This prevents too much water from evaporating through the open leaves. This ingenious mechanism allows plants to survive during dry periods.
Hidden support networks
Plants exhibit a special form of intelligent social behavior. For example, felled trees that no longer receive nutrients through photosynthesis because they no longer have leaves or an intact trunk can still survive. This is possible because the roots of the damaged tree communicate with the roots of neighboring trees. The neighboring trees then provide the necessary nutrients to the damaged tree.
Protection from predators
Plants also communicate to protect themselves from dangers such as predators. For example, acacias in Africa have developed an interesting way to protect themselves from predators such as giraffes. When giraffes start eating an acacia’s leaves, the tree sends electrical impulses to the surrounding trees. These signals act as a warning. The neighboring trees respond by producing bitter substances in their leaves. These bitter substances make the leaves inedible to the giraffes, thus protecting the trees from being eaten.


What can we learn from plants?
The strategic intelligence of plants is not only a source of inspiration, it also challenges us to question our traditional understanding of nature, economics and society. By integrating the principles of the plant world into our daily actions, we can create more sustainable and life-enhancing systems that contribute to a better future.
It is also important to recognize that plants, with their intelligent mechanisms, especially photosynthesis, are vital to nature and humans. Without this cycle, which provides oxygen and food to a wide range of living beings, we humans would not be able to survive. This underscores the central role of plants in our ecosystems. Plants teach us that without them, there would be no life.
OUR RECOMMENDATIONS FOR YOU
5 min































.png)

