
Skin Concierge
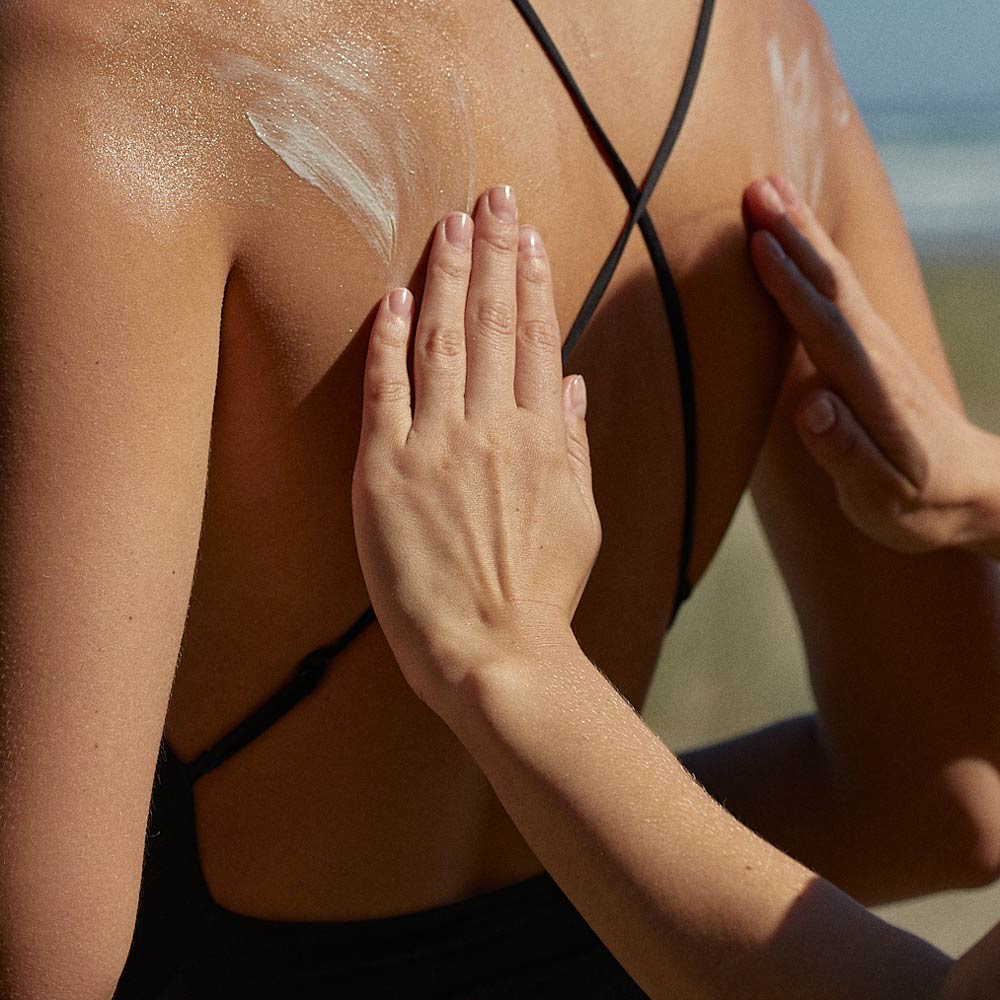
Natural sun care for healthy skin
Why is sunlight so important to our organism?
Our body needs the sun’s high-energy UV light to produce healthy vitamin D, while excessive sun exposure poses a significant health risk. Find out how you can prevent skin damage and still enjoy the benefits of the warming light.
The daily rise and set of the sun is one of the few reliable events in our lives. Despite this, we often pay too little attention to the effects of sunlight on our health. The numerous benefits of the sun range from energy supply for photosynthesis in plants and bacteria to vitamin D production for humans. But as with most biological processes, the right dose is the decisive factor: Excessive exposure to sunlight is a serious health risk. Sunlight, especially UVA and UVB radiation, can cause sunburn, premature skin aging, eye damage, a weakened immune system, photo-allergic and phototoxic reactions, and even skin cancer.
Precious vitamin D
Our bodies need the sun’s energy-rich UV rays to produce vitamin D. This precious vitamin is essential for cell health and bone strength. The lighter your skin tone, the faster your daily vitamin D requirement is met: Very fair skin types only need 10 minutes of direct exposure per day. However, sunscreens with SPF 8 or higher almost completely inhibit the production of this healthy vitamin in the body.
*Vitamin D is not a vitamin in the classical sense, but rather the preliminary stage of a hormone produced in the body, which is “activated” by the sun’s UVB rays. The UVB rays penetrate the upper layers of the skin, where they first convert the body’s hormone cholesterol into the pre-vitamin D3. This is then converted into vitamin D by the contemporaneous generated heat of the infrared rays.
Natural antidepressant
According to studies, the production of the messenger substance serotonin in the brain, an important neurotransmitter that lifts our mood, is directly influenced by the amount of sunlight. The warming rays brighten our mood, the level of serotonin is higher on sunny, bright days than on overcast or cloudy days. In addition, sunlight regulates our biorhythm. The light influences the production of hormones that are necessary for activity and sleep.


Effective sun care for lasting protection
Free radicals and their effect on our skin
Natural daylight is made up of an almost continuous spectrum of light waves. However, our eyes can only perceive a small part of it as colour, with each colour representing a specific wavelength. High-energy, short-wavelength light is invisible to us but can cause significant damage at a cellular level.
Short-wave UV light has a strong oxidizing effect. When it reaches our skin cells, it creates free radicals. These are unstable molecules with unpaired electrons that tend to oxidise other molecules by ‘stealing’ electrons. This can damage cell structures and their components, such as proteins, lipids and DNA.
Oxidative stress contributes to skin aging
When there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralise or scavenge them with antioxidants, a condition called oxidative stress occurs. The skin is constantly exposed to oxidative stress, both from internal factors such as metabolic processes and external factors such as pollution and sunlight.
Oxidative stress accelerates the ageing process of the skin. The damage caused by free radicals leads to the destruction of collagen and elastin, the proteins that give skin its firmness and elasticity. This can lead to the formation of wrinkles, sagging skin and unwanted pigmentation. In addition, excessive production of free radicals weakens the skin’s barrier, making it more susceptible to irritation.
Long-term and repeated exposure to UV rays and the associated oxidative stress can even contribute to the development of skin cancer. Since free radicals can damage the DNA in skin cells, they increase the risk of mutations.
Natural broad-spectrum sun protection
Our sun care products are designed to provide broad-spectrum protection against the full spectrum of light to protect your skin from premature ageing and the damaging effects of UV rays. As certified natural cosmetics, they are free from microplastics, nanoparticles, silicones, parabens, mineral oils and potentially harmful chemical filters such as oxybenzone, octinoxate or octocrylene.
Buddleja: Power ingredient for summer skin
A key ingredient in all our suncare products comes from the flowers of buddleja.
It is known for its richness in verbascosides and echinacosides. It not only protects the plant from UV and IR-A rays, but its powerful antioxidant action protects the skin from both natural and artificial light. Among other things, it can reduce the negative effects of HEV light. HEV stands for High Energy Visible Light, also known as blue light, which is emitted by digital screens such as computers, smartphones, televisions and LED lights. In addition, Buddleja has soothing, calming and regenerating properties, helping to reduce skin irritation and redness while supporting the skin’s moisture barrier.

The ABC of UV radiation
There are two types of radiation in sunlight that have a medicinal effect on the skin: UV radiation and infrared radiation. UV radiation plays an important role in the production of vitamin D, while infrared radiation is responsible for the feeling of warmth.
How much UV radiation the skin actually receives depends on various factors summarized in the UV index: the time of day, the season, the geographical location, the altitude, weather conditions and the ozone layer. The UV index ranges from 0 (low radiation intensity) to 11+ (extreme UV radiation), with sun protection recommended from a UV index of 3 or higher.
UVA rays
- Act with approximately the same intensity throughout the day
- Can almost freely pass clouds, mist, windows and glass
- Ensure immediate, short-term tanning of the skin
- Activate the precursor stages of melanin in the upper skin cells
- Deeply enter the lowest layer of the skin (dermis)
- Play an essential role in long-term damage such as premature skin aging, sun allergies, eye damage and weakening of the immune system
UVB rays
- Vary in intensity throughout the day
- Stimulates the production of new melanin
- Ensure a long-lasting tan
- Supplies the skin with the energy to produce vitamin D
- Causes the formation of free radicals everywhere in the epidermis
- Main cause of acute light damages such as sunburn, skin cancer and damage to the eyes and retina
UVC rays
- Are very aggressive
- Only occur rarely, as the ozone layer normally filters out the dangerous UVC rays


How do sunscreens work?
The ideal sun protection factor
The appropriate sun protection factor (SPF) depends mainly on your skin type and the UV index of the sun. The higher this index and the fairer the skin, the higher the sun protection factor should be. The pigmentation of the skin partly indicates the self-protection of the skin from sunlight. Every skin has a natural self-protection time. The fairer the skin type, the shorter the skin’s natural self-protection time.
*The sun protection factor (SPF) multiplied by the skin’s natural sun protection (in minutes) indicates the period of time during which one can stay in the sun without the risk of UV-induced skin damage. The use of sunscreen, when used correctly, can, therefore, reduce the harmful effects of UV radiation on health. However, even a high SPF never completely protects the skin from solar irradiation.
Mineral or chemical sun filters
There are generally two types of sunscreen: organic-chemical and mineral-physical sunscreens.
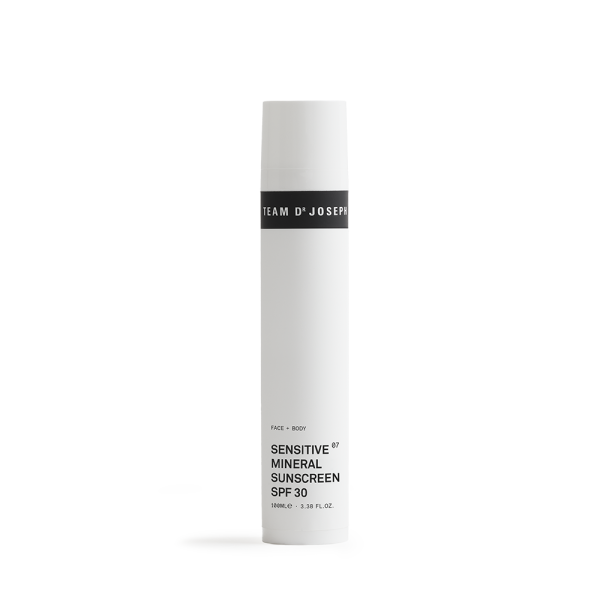
Mineral sunscreens use natural mineral particles such as zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. These particles act like a mirror to reflect and scatter harmful UV rays, preventing them from penetrating the skin. Our bio-certified Sensitive Mineral Sunscreen SPF30, which is based exclusively on mineral filters, contains transparent non-nano zinc oxide to provide broad-spectrum protection against UVA and UVB rays.
Organic chemical sunscreens, on the other hand, are made up of chemical compounds that have the ability to absorb certain wavelengths of UV light and convert it into heat. In our High Protection Sun Cream SPF30 and Ultra Light Sun Block SPF50+, we use both mineral and chemical filters for sun protection.

Applying sunscreen correctly
Chemical sunscreens should always be applied generously to the face and body 15 to 30 minutes before going outdoors. Mineral sunscreens work immediately after application. To maintain sun protection, it is important to reapply suncream several times a day, especially after being in the water or sweating heavily. However, reapplying sunscreen does not extend the amount of time you can spend in the sun without protection. And don’t be complacent: our cells remember any damage they have suffered from sun exposure.
Checklist for sun lovers
- Always use a suncream with an appropriate sun protection factor.
- UV radiation is harmful in all seasons. Don’t forget to apply suncream, even if you are enjoying the first rays of sunshine in spring or rushing down the slopes in winter.
- Don’t forget to use sun protection even on cloudy days. More than 90% of UV radiation still passes through a light cloud cover.
- Avoid the intense midday sun.
- Protect your eyes from UV light by wearing sunglasses with light protection.
- Apply cream all over your body. Pay attention to often forgotten areas such as the back of your hands and feet or your ears.
- A sun hat keeps a cool head.
- Don’t forget the after sun.
OUR RECOMMENDATIONS FOR YOU
2 min









































.png)

